This article aims to provide you with the concept of the Critical Path, including how to identify Critical Path tasks and how to effectively manage them.
|
Skip Ahead to: What does the Critical Path show? How is a Critical Path calculated? |
Overview
Tasks that can affect the project’s finish date are called critical tasks. Critical tasks make the critical path of the schedule.
A task is considered a critical task if it satisfies any of the following conditions-
- A task with no slack or float.
- A task having the inflexible constraint (Must Start On and Must Finish On) applied to it.
- A task with a “Fixed Dates” task type.
- The finish date of the task is the same as or beyond the deadline date of the project.
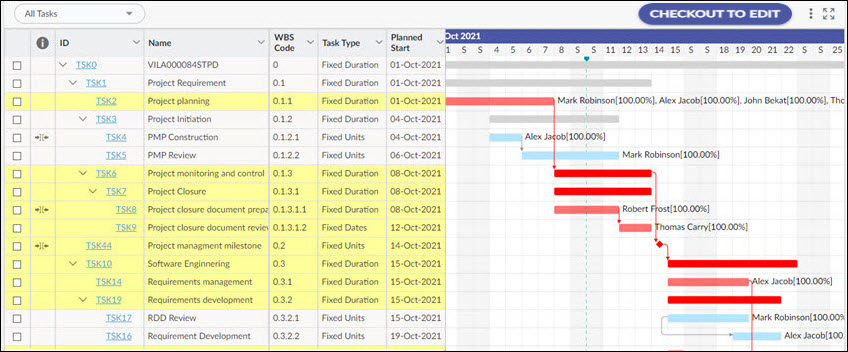
Critical Tasks are highlighted in red in the Gantt view.
Notes:
- A critical task no longer remains the critical task if it is completed because in that case, it can’t affect the successor task or the project finish date.
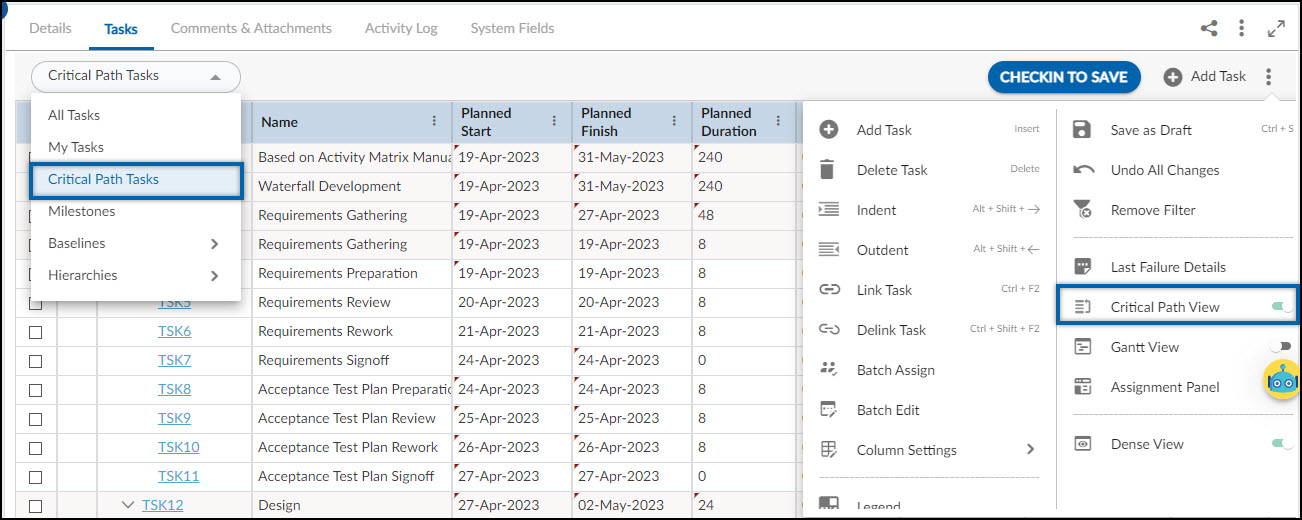
- The Critical Path Tasks and Critical Path View options are only available in the Advanced scheduling type.
What is Slack/Float?
Slack, also known as float, is the amount of time a task can delay without affecting other tasks. This is considered a buffer time for a task and is useful if the task is likely to be delayed. The project calculates the float/slack automatically when you schedule a task. The task with slack/float doesn’t affect the critical path of the project.
In other words, any task with some slack has some buffer time which can be used if your task is being delayed. A task with no slack is considered a critical task. Such tasks can affect the project finish date as the delay in a critical task affects the critical path which further affects the project’s finish date.
If you want your project to be finished on time, then you can optimize the tasks that have slack and are not on the project’s critical path. You can delay such tasks (having free slack) and use their resources in critical tasks to get them done so that you can save the schedule from slipping.
The total slack can be negative or positive. The negative slack indicates the buffer time of the task is negative which means the task is not scheduled with enough time and needs more time to be completed.
Note: If the Constraints to be honored over dependencies preference is Off and a task has a constraint applied to it and the first task finishes too late to let the second task begin on the constraint date, then the negative slack will appear. This negative slack will further constrain the finish date of the project.
What is a Critical Path?
A critical path is a series of tasks that determines when the project will end. In other words, the critical path determines how long a project will go. Each task on the critical path directly impacts the end date of the project so if any task moves, the end date of the project also moves.
- One project can have multiple critical paths if there are multiple hierarchies in a project that have critical tasks.
- The critical path is highlighted in red in the Gantt chart view.
- If a summary task has all its tasks as critical tasks then the entire task will be highlighted as a critical task because all its subtasks are critical.
- A task with no slacks or float means that the task is ending on the project finish date.
You can view the critical path task by clicking the More Options icon and selecting the Critical Path View option. You can also select the Critical path view from the All Task to view the drop-down list on the top bar.
Important points:
By default, there is only one critical path in the project which affects the project’s finish date. However, you can see multiple critical paths in your project if you have multiple critical hierarchies.
What does the Critical Path show?
The critical path shows the series of critical tasks that may affect the end date of the project. It helps you know which tasks can affect the project’s end date and whether your project will finish on the set date or not.
Tip: If you want to finish your project on time, then it is important to pay attention to the tasks on the critical path. If a critical task takes more than expected time to complete or the resource assigned to the task is unavailable for any reason, then the project is unlikely to be finished on the original finish date.
Tasks on the critical path are usually linked to each other. However, there might be more than one sequence of critical tasks. In the case of multiple sequences of critical tasks, the one that will finish at the very last is considered the project’s critical path.
Note: The critical path of a project may change if –
- The critical tasks in the critical path are completed.
- The tasks in other sequences are delayed.
How is a Critical Path calculated?
The slack on a task is calculated using the early finish and the late finish dates of the tasks. The early finish date of a task is the earliest date on which the task can be finished based on its duration and start date. Similarly, the late finish date of a task is the latest date the task can finish without impacting the project’s finish date.
Slack on a task is determined by the difference between the early finish date and the late finish date of the task. In the case of critical tasks (with 0 slack), the early finish date and the late finish date are the same.
How to shorten the Critical Path?
If you want your project to finish on time, then you need to shorten the critical path so that the project finishes on an earlier date. For that, you have to bring in the finish dates of the critical tasks. Bringing in the critical task’s dates is also called the crashing of the project. You can shorten the critical tasks by-
- Shortening the task duration or working on it.
- Changing the task constraint to a flexible constraint.
- Break a task into smaller tasks that can be easily worked upon by more than one resource at a time.
- Updating the task dependencies to allow more flexibility for scheduling.
- Setting the lead time between the predecessor and successor.
- Scheduling overtime.
- Assigning more resources for critical tasks so that they can be completed on time.
Note: If you bring in the finish date of the critical path, a different sequence (of tasks) might become the new critical path for the project.
Can a Project Have Multiple Critical Paths?
By default, a project has only one critical path, but if there are more than one series of critical tasks then these series of tasks are considered multiple critical paths.
Note: Changing the finish date of the second critical path might not affect the project’s finish date.